Introduction
Fermented foods are produced through a natural process in which microorganisms such as bacteria or yeast break down sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol. This process enhances flavor, improves shelf life and increases nutritional value.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Many naturally foods contain these beneficial microbes, making them valuable for digestive health.
Common examples include:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Naturally fermented pickles
- Traditional fermented drinks like kanji
These foods are often referred as probiotic foods for digestion because they support the balance of gut bacteria.
Improving Gut Health
1. Supporting Beneficial Gut Bacteria
The human digestive tract contains trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for digestion, immunity, and nutrient absorption. Research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) highlights that diet plays a major role in shaping gut bacteria composition.
When beneficial bacteria thrive, overall gut health improves. They introduce beneficial bacteria into the digestive system. These microbes help:
- Improve digestion
- Produce certain vitamins
- Compete with harmful bacteria
- Support immune defenses
2. Increasing Microbiome Diversity
Microbiome diversity refers to the variety of different bacterial species living in the gut. Greater diversity is often linked to better digestive and immune health.
A scientific review published in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (source) explains that these foods can influence the composition and activity of gut microbiota, potentially enhancing microbial diversity and reducing inflammation.
Natural Fermented Foods
Some of these include:
- Yogurt and kefir (rich in live cultures)
- Sauerkraut and kimchi (contain probiotics and fiber)
- Miso and tempeh
- Naturally fermented pickles
These foods are fermented by bacteria or yeast, producing beneficial compounds such as lactic acid that aid digestion and improve nutrient availability.
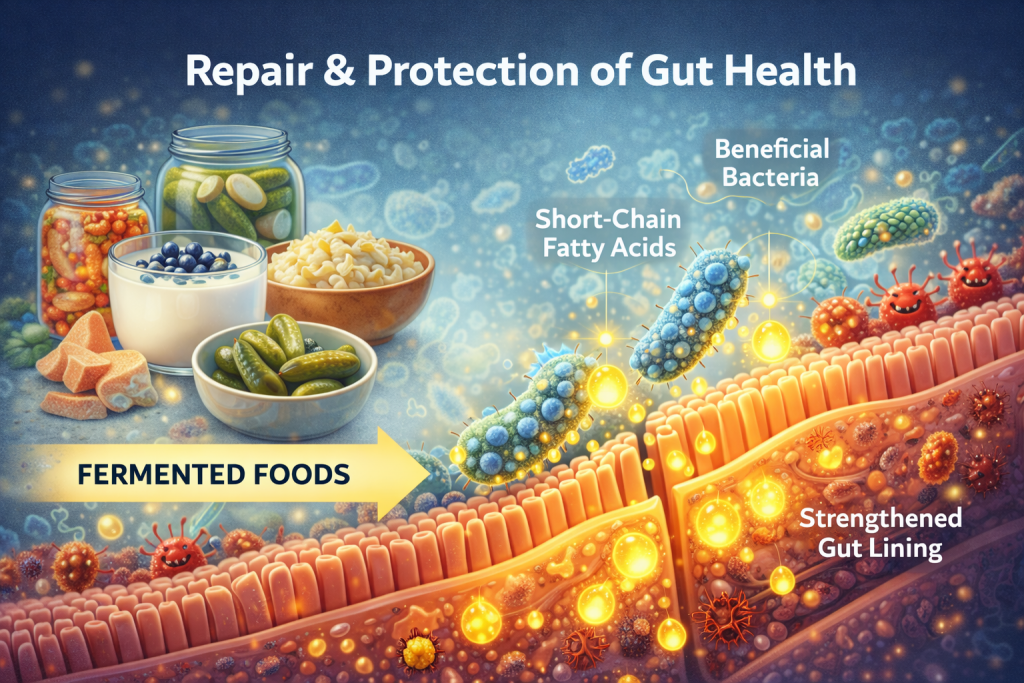
Repair and Protection Of Gut
Fermented foods may support the intestinal lining and enhance digestive efficiency. Beneficial bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids, which help maintain the gut barrier and reduce inflammation.
Different educational resources emphasize that a balanced diet rich in probiotic and fiber-containing foods plays a key role in maintaining gut integrity and immune function. While these foods are not a cure for digestive disorders, they can be part of a natural strategy to strengthen gut health over time.
Fermented Foods vs Probiotic Supplements
Many people wonder whether these foods are better than probiotic supplements. Supplements provide concentrated strains of bacteria, but whole fermented foods offer additional nutrients such as vitamins, enzymes, and fiber.
Whole foods may:
- Improve digestion naturally
- Enhance nutrient absorption
- Provide supportive compounds beyond probiotics
For most people, obtaining probiotics from food sources is a practical and sustainable option, while supplements may be helpful under medical supervision.
Duration Required To Improve Gut Health
Improving gut health is not immediate. Some individuals may notice reduced bloating or better digestion within days or weeks. However, long-term improvements in gut microbiome diversity require consistent dietary habits. Consistency matters more than large quantities.
Research cited by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggests that regular dietary patterns influence the microbiome gradually. Eating small portions of it daily, along with fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, supports lasting results.
Is There Any Downsides?
Although they are generally safe, consuming them in excess may cause temporary bloating, especially for beginners. Some of these are, particularly pickles, may contain high levels of salt.
Guidance from Harvard Medical School recommends moderation and dietary balance to avoid excessive sodium intake. Starting slowly allows the digestive system to adjust.
Tips For Daily Diet
To maximize the benefits for gut health:
- Start with small servings of yogurt or kefir
- Add fermented pickles as a side dish
- Combine these with fiber-rich meals
- Eat them regularly rather than occasionally
- Maintain a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
Conclusion
Fermented foods and gut health are closely connected. By introducing beneficial bacteria, increasing microbiome diversity, and supporting digestion. As they offer a natural way to strengthen the gut. Including these in your daily routine—whether yogurt, kefir, kimchi—can be a simple yet powerful step toward better digestive health. Small, consistent changes today can lead to a healthier gut tomorrow.


