Have you ever wondered how your body retains heat in cold weather? Whether you’re walking in the snow or just trying to stay warm in a chilly room, your body has built-in mechanisms to help maintain a stable temperature—even when the environment turns freezing.
Let’s explore how heat flows from hot to cold, the role of human skin in maintaining body temperature, and how exercise and environmental conditions affect our body’s thermal regulation.
Why Does Heat Flow from a Hot Body to a Cold Body?
According to the laws of thermodynamics, heat always flows from a hot body to a cold body until thermal equilibrium is reached. This is because energy naturally moves from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration.
So why does heat flow from hot to cold?
- The molecules in the warmer object (like your body) are more energized.
- These molecules transfer their energy to the cooler environment through conduction, convection, or radiation.
Under what conditions does heat flow from a hot body to a cold body?
Any time two objects at different temperatures come into contact—or are near each other—heat will flow from the warmer to the cooler object until both reach the same temperature.
How Human Skin Maintains Temperature in Cold Conditions
Your skin plays a critical role in thermoregulation, which is the body’s ability to maintain a constant internal temperature.
How human skin maintains temperature in cold conditions:
- Vasoconstriction: Blood vessels in the skin narrow, reducing blood flow near the surface to minimize heat loss.
- Shivering: Muscles contract rapidly to generate heat.
- Goosebumps: Tiny muscles around hair follicles contract, trapping a layer of insulating air close to the skin.
- Fat Insulation: The fat layer under the skin acts as a barrier to retain body heat.
When you are cold, how does your skin keep heat in your body?
By limiting blood flow to the skin’s surface (vasoconstriction) and activating shivering, your body tries to conserve core temperature.
How to Maintain Body Temperature in Cold Weather
Here are some natural and behavioral ways to maintain body temperature in cold weather:
- Wear layers: Traps heat and reduces exposure to cold air.
- Stay dry: Moisture increases heat loss.
- Keep moving: Physical activity boosts metabolic heat production.
- Consume warm food and drinks: Helps fuel the body and maintain warmth.
How Long Does Heat Flow from a Hot Body to a Cold Body?
The duration of heat flow depends on:
- The temperature difference between the two bodies.
- The thermal conductivity of the materials involved.
- The surface area and time of contact.
For example, when sitting on a cold surface, heat flows from your body into the seat until both reach a similar temperature.
What Happens When the Body Becomes Too Hot?
The reverse condition—overheating—can lead to heat exhaustion or heat stroke. The body responds by:
- Vasodilation: Expanding blood vessels to release heat.
- Sweating: Evaporation of sweat cools the skin.
But in cold environments, these functions are suppressed to conserve heat.
How Does Heat Flow from Hot to Cold?
Let’s break down the three ways:
1. Conduction
Heat is transferred directly through contact—like your body warming up a cold blanket.
2. Convection
Heat is lost to the air moving around your body (e.g., wind chills).
3. Radiation
Your body emits infrared radiation, which can be absorbed by surrounding surfaces.
How Temperature Affects the Body During Exercise
How temperature can affect the body in different types of exercises depends on:
- Cold weather: Muscles become stiffer, increasing injury risk. You burn more calories to stay warm.
- Hot weather: Excessive sweating can lead to dehydration and overheating.
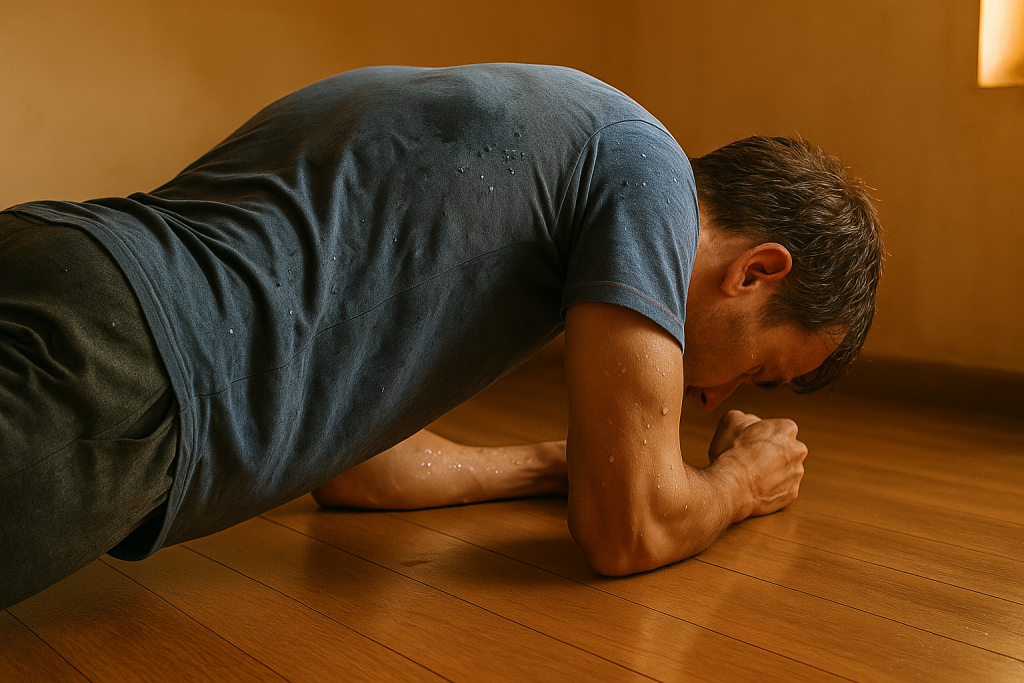

In both cases, your body works hard to maintain internal balance.
FAQ Quick Recap:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How does the body retain heat in cold weather? | By reducing blood flow to the skin and triggering muscle contractions (shivering). |
| How does heat flow from hot to cold? | Via conduction, convection, and radiation—until thermal equilibrium is reached. |
| What happens when the body becomes too hot? | It sweats and dilates blood vessels to release excess heat. |
| How to maintain body temperature in cold weather? | Wear layers, stay dry, move regularly, and consume warm foods. |
Summary
The human body is a brilliant self-regulating system. Through vasoconstriction, shivering, and skin insulation, it retains heat in the cold. Understanding why heat flows from a hot to cold body, and how skin maintains body temperature in cold conditions, can help us make better lifestyle and clothing choices to stay healthy and comfortable.



Hi, i think that i noticed you visited my web site thus i got here to “return the desire”.I am trying to find things to enhance my website!I assume its good enough to make use of some of your ideas!!